4.1 Multi-Country Numbering Plan
Since numbering plan and requirements for numbering vary from country to country, multi-country numbering plan adaptation functions are created.
The relationship between MSC and its external interfaces is illustrated in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 MSC and its external interfaces
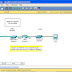
Structure diagram of number processing is shown in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 Structure of number processing
The diagram shows that number processing, if considered as an integrated system, interacts with the following external interfaces:
- MS side (MS dials the number), trunk side (all office directions in [Office Direction Table] except BSC direction),
- MAP side (forwarded-to number obtained from HLR or VDB, and MSRN obtained from HLR),
- SCP side, PRA, and bill.
The input side should be capable of pre-analyzing the numbers input from MS side, trunk side, MAP side and SCP side, so that the core number analysis system can analyze the numbers. The output side should also be capable of converting the numbers output to the MS side, trunk side, MAP side, SCP side, PRA and bill to meet the requirements of external entities.
Number processing includes three phases: "Number pre-processing", "Number analysis" and "Send-number processing". In "Number pre-processing" phase, numbers from the signaling are normalized and output to "Number analysis" part. The step suceeding to "number analysis" is "send-number" processing. In this step, numbers are converted into the format applicable to the signaling of various countries and various exchanges and particular information can be added to the numbers (In principle, only the format of sent-number is changed, while the number saved in the switch remains unchanged.)
Apart from the above functions, Multi-country numbering plan can be used to add, delete and change a number, and can also be used to substitute and insert a number. This function can be used in all the three phases.
4.1.2 Index between Multi-Country Numbering Plan Tables
I. Index between Number Pre-Analysis and Number Change (Conversion) Table
Figure 4-3 Index between number pre-analysis and number change table
II. Index between Caller IMSI Analysis and Number Change Table
Figure 4-4 Index between caller IMSI analysis and number conversion table
III. Index between CDR Number Format and Number Change Table
Figure 4-5 Index between CDR number format and number change table
4.1.3 Index Between Caller Number Presentation Processing and Number Change Table
Figure 4-6 Index between caller number processing and number change table
4.1.4 Index between Outgoing Trunk Sent-Number Processing and Number Change Table
Figure 4-7 Index between outgoing trunk sent-number processing and number change table
4.1.5 Index between Other Number Format Table and Number Change Table
Figure 4-8 Index between other number format table and number change table
4.2 Task Procedure
4.2.1 Number Pre-Analysis
The following diagram shows the table query sequence in number pre-analysis part:
Figure 4-9 Number preprocessing
Note:
The dotted lines indicate that functions of number conversion module can be used to convert numbers at all analysis phases. The solid lines indicate the number analysis sequence.
For “number attributes analysis”, only when the number content and number attributes from the trunk are strictly consistent, “number attributes analysis” part can be used to normalize the number attributes. For IMSI analysis, currently only when an intelligent call is triggered by IMSI, will the IMSI be analyzed. The purpose of number pre-analysis is to normalize numbers from different call sources for further analysis.
4.2.2 Number Attributes Analysis
I. Description
A number from the trunk includes number content and number attributes. If the number content is strictly consistent with the number attributes, the number can be normalized and converted according to the number attributes and number prefix. Numbers can be normalized and converted in two ways:
1) They can be normalized as subscriber number, national number without toll prefix, national number with toll prefix, international number without international prefix, and international number with international prefix.
2) They can be converted more flexibly with the help of number change table.
II. Example
1) Simple conversion
Normalize all incoming numbers as international numbers without international prefix, regardless of the numbers of the calls and number attributes:
Add a record to the Called Nature Analysis table. [Called Number] and [Called Number Nature of Address] can be conFigured in wildcard, and [Called Number Format] can be conFigured as INT_NO_PRE, as shown in the following diagram:
Figure 4-10 Called Nature Analysis table
2) Flexible conversion
Change the subscriber number prefix 8807 into 9908, conFigure the data as follows:
Figure 4-11 Called Nature Analysis table
4.2.3 Normalize Numbers Obtained from MAP Side
I. Description
The numbers obtained from the MAP side include MSRN (from HLR) and forwarded-to numbers (from HLR or VLR). As defined in the protocol, all numbers obtained from the MAP side are in the format of international number, i.e. CC+ NDC+ SN (for MSISDN) or in CC+Areacode + SN format (for PSTN).
For Huawei MSC, a default number conversion process is designed for the numbers obtained from the MAP side (refer to TP-004). If the MAP signaling is not standard, numbers (MSRN and forwarded-to number) from the MAP side must first be normalized in the format of international numbers, then the default number conversion can be performed.
II. Example
In an MSC office in Moscow, CC = 7, NDC = 095, MSISDN = 7-095-9208604, and the national prefix = 8. In the signalling transmitted between the local MSC and the HLR, it is observed that the obtained forwarded-to number is 80959208604, not in the format of international number. Therefore, it must be converted into an international number through number pre-analysis, and the data configuration is as follows:
Figure 4-12 DN pre-analysis table
Figure 4-13 Number change table
4.2.4 Normalize Forwarded-to Number and MSRN/HO Number
I. Description
All MSRN, HO numbers or forwarded-to numbers obtained from the MAP side must be in or be converted into the format of international number, i.e. CC+NDC (for MSISDN)+SN or Area code (for PSTN)+SN. If not, the method described in TP-003 must be applied to normalize the number to international format. For Huawei MSC, a default number conversion process is designed for the numbers obtained from the MAP side, which can be regarded as a "black box" process. The principle is as follows: if it is an international call, the number input in the "black box" should be added international prefix. If it is a national call, the international number input in the "black box" should be converted into the format of national number. See the Figure below.
Figure 4-14 Number conversion
Input: MSISDN/MSRN/HO: CC+NDC+SN, with the attribute as INT
PSTN: CC+ Area code + SN, with the attribute as INT
Output:
MSISDN/MSRN/HO: NDC+SN, with the attribute as NAT
PSTN: national prefix + area code + SN, with the attribute as NAT.
International numbers (including MSRNs of other countries): international prefix + international number.
Here, if this PSTN is a local PSTN, whether to remove the local area code is decided by the software parameter DB internal parameter 1 bit 8 (if the software parameter is 1, the local area code will be removed from the local PSTN number; if it is 0, the local area code will not be removed from the local PSTN number, which will be added with the national prefix. The default setting is 1).
Note:
1) Number pre-analysis at the MAP side is necessary only when the number received in the MAP signalling is not in the format of international number.
2) When the number being analyzed is a forwarded-to number and the result of number change in the Black Box fails to meet the subsequent DN analysis, i.e. querying of Called number analysis fails, further number change can be performed at Call forward side.
II. Example
Office: The MTS office in Moscow, CC = 7, NDC = 902, national prefix = 8, international prefix = 810, the AreaCode of Moscow = 095, the AreaCode of Krasnoyarsk = 3912, an MSRN = 79021980000, a PSTN of Moscow = 70957923333, a PSTN telephone of Krasnoyarsk = 73912555517, and an MSISDN number = 79029310002.
Note:
A calls B, and the call is forwarded to C.
B is forwarding number. C is forwarded-to number.
Case 1: Local MSC receives the MSRN 79021980000 allocated by the local office, After the processing of Black Box, the number is 9021980000. Then the format of MSRN of the local office conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] should be NDC+SN.
Case 2: CFU occurs at the local office, and the destination is local PSTN of Moscow. The forwarded-to number the local MSC receives from the HLR is 70957923333, which is changed in Black Box to obtain the result 7923333. Then the format of the local PSTN number conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] should be in SN format. If the format of the local PSTN number conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] is national prefix + Area Code + SN, the default value of software parameter can be changed: modify the software parameter DB internal parameter 1 bit 8 as 0, indicating that, the local area code is not removed from the number
forwarded to the local PSTN and the national prefix is added to it during the number change in the Black Box.
Case 3: CFU occurs at the local office, and the destination is domestic toll PSTN. The forwarded-to number local MSC receives from the HLR is 7391255517, which is changed in Black Box to obtain the result 8391255517. Then the format of the domestic toll PSTN number conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] should be national prefix + Area Code + SN.
Case 4: CFU occurs at the local office, and the destination is an MS of the MTS of Moscow. The forwarded-to number local MSC receives from the HLR is 79029310002, which is changed in Black Box to obtain the result 9029310002. Then the format conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] (MSISDN format of MTS in this network) should be NDC+ SN.
Case 5: The local office originates a call to an MTS subscriber roaming in China. The format of MSRN received by local MSC is CC + NDC + SN (86-139-02712345), which is changed in Black Box to obtain the result 810-86-139-02712345. Then the format of MSRN of foreign countries conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] should be international prefix + CC + NDC + SN. Generally only the international prefix is to be conFigured.
Case 6: CFU occurs at the local office, and the destination is a number of international mobile subscriber. The format of MSRN received by local MSC is CC+NDC+SN (86-139-22895400), which is changed in Black Box to obtain the result 810-86-139-22895400.Then the format of international number conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] should be international prefix + CC + NDC + SN. Generally only the international prefix is to be conFigured.
4.2.5 Preprocessing of Local-originated Number
I. Description
Mobile subscribers dialing modes allowed vary from country to country and operator to operator. The most common one is that multiple formats are allowed for the same number. For example, to dial a local MS, the dialing modes may be:
SN,
NDC+SN,
Domestic Prefix + NDC+SN,
International Prefix + CC+ NDC+ SN, or
'+' + CC+NDC+SN, etc.
To facilitate number analysis, numbers in various formats must be normalized into one format before querying [Called Number Analysis Table]. The recommended standards are as follows:
1) MSISDN of local network:
The format in [Called Number Analysis Table] is NDC+ SN. MSISDNs in other formats are to be normalized into this format through number pre-analysis.
2) Number of local PSTN:
There are two cases:
a) If the numbering scheme of the country where the called is located specifies that the mobile subscriber must dial the local area code when initializing a local call, the local PSTN numbers must be conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] in the format: Domestic Prefix + Area code + SN.
b) If the numbering scheme of that country specifies that the mobile subscriber does not need to dial the local area code when initializing a local call, the local PSTN numbers can be conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] in the format of SN.
3) Domestic toll PSTN number:
It is recommended to conFigure it in [Called Number Analysis Table] in the format: Domestic Prefix + Area Code + SN.
4) Numbers of other national networks:
For direct outgoing calls, conFigure it as required by the peer end.
5) International subscriber number:
It is recommended to conFigure it in the format of International Prefix + International number in [Called Number Analysis Table].
II. Example
Office: Mfone Company Cambodia
CC = 855, NDC = 11, International Prefix = 165, MSISDN segment of local network = 00XXXX, an MSISDN number = +855-11-001232
Permitted dialing modes:
1) 001232;
2) 11-001232;
3) 855-11-001232;
4) 165-855-11-001232;
5) '+' + 855-11-001232
In [DN Pre-analysis] table, all the numbers in the above five formats are normalized into format 2) and data configuration is shown in the following Figure:
Figure 4-15 Configuration of DN pre-analysis table
Figure 4-16 Configuration of Number change table
4.2.6 Preprocessing of Incoming Numbers
I. Description
If the MSC is directly connected to PSTN and other office directions, the numbers sent from other office directions to the local office may have a variety of formats. The specific format is decided by the peer office.
For example, the number formats for a mobile subscriber of local network may be:
SN,
NDC + SN,
Domestic Prefix + NDC+SN,
International Prefix + CC + NDC + SN,
etc.
To facilitate number analysis, the numbers in various formats must be normalized into one format before number analysis (i.e. before querying [Called Number Analysis Table]). The recommended standards are as follows:
1) MSISDN of local network:
It is in the format NDC + SN in [Called Number Analysis Table]. MSISDNs in other formats are to be normalized into this format through number pre-analysis.
2) Number of local PSTN (assume that local MSC also serves as a tandem office):
There are two cases:
a) If the numbering scheme of the country where the called is located specifies that the mobile subscriber must dial the local area code when initializing a local call, the local PSTN numbers can be conFigured in the format of Domestic Prefix + Area Code + SN in [Called Number Analysis Table].
b) If the numbering scheme of that country specifies that the mobile subscriber does not need to dial the local area code when initializing a local call, the local PSTN numbers can be conFigured in the format of SN in [Called Number Analysis Table].
3) Domestic toll PSTN (if local MSC also serves as a tandem office):
The format recommended to be conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] is Domestic Prefix + Area Code + SN.
4) MSISDN of other national networks (if local MSC also serves as a tandem office): For direct outgoing calls, it is necessary to conFigure them as required by the peer end.
5) International subscriber number (if this MSC also serves as a tandem office):
The recommended format to be conFigured in [Called Number Analysis Table] is International Prefix + International number.
II. Example
In an MSC,
CC = 998, NDC = 90, Old NDC = 590, International Prefix = 810, MSISDN segment of home network = 185XXXX, an MSISDN number = +998-90-1850123, Domestic Prefix = 8
Formats of MSISDNs received from PSTN office direction (ISUP signalling is used for local MSC and PSTN) include:
1) 1850123;
2) 90-1850123;
3) 8-590-1850123;
4) 810-998-90-1850123.
Data configuration: In [DN Pre-analysis] table, all the numbers in the above four formats are normalized into format 2).
Data configurations are as follows:
Figure 4-17 Configuration of [DN Pre-analysis] table
Figure 4-18 Configuration of [Number Change] table
4.2.7 Number Pre-Analysis According to IMSI
I. Description
Whether an MS is a PPS subscriber is identified according to IMSI in some countries, i.e., the attributes of a subscriber is identified according to IMSI segment or a certain bit of IMSI.
In order to analyze IMSI, [IMSI Bits Analysis] and [IMSI Segment Analysis] tables are added. When subscribers who have registered at VDB as callers, IMSI analysis table will be queried.
II. Example
Whether a caller is a PPS subscriber and the attributes of the caller are identified according to a specific bit of IMSI. For example,
52000**1******* Indicates common subscriber, and
52000**9******* Indicates PPS subscriber.
1) If it is a PPS subscriber, the call should be routed to an MSC acting solely as SSP in OVERLAY mode for call processing.
Specific configuration is shown in the following diagram:
Figure 4-19 IMSI bits analysis table
For a call initialized by a PPS subscriber, convert the called number by adding a prefix to it according to the assigned Called number change index (100, for example). Then with this number prefix, the call can be routed to the MSC acting solely as SSP according to the configuration of [Called Number Analysis Table].
2) The local MSC supports SSP function, and intelligent calls are triggered at local office. The configuration is shown in the following Figure:
Figure 4-20 IMSI bits analysis table
If the intelligent call is triggered at the local office, whether the caller is a PPS subscriber is decided according to IMSI. The software parameter CCB_PARA_12_BIT14 should be modified as 0, and the data of all number segments should be conFigured in SCP addressing table. Only for PPS subscribers will SCP addressing table be queried.
3) IMSI number segment analysis
The configuration is shown in the Figure 4-21.
Figure 4-21 IMSI segment analysis table
To analyze the number by number segment, the software parameter DB parameter 0bit must be modified as 0. But, to analyze the number by number bit, the software parameter DB parameter 0bit must be modified as 1.
4.2.8 Use of Call Source Code
I. Description
Subscriber sets with the same call attributes can be grouped into one category of call source. At present the concept of call source refers to the incoming trunk or a specific location area/cell that originates a call. It is categorized according to the geographical property. Generally, several trunk groups belong to the same call source, or all location area/cells belong to one call source. Each call source has an integer code, called call source code.
Therefore, the call source can be defined in two tables: one is the [Trunk Group] table, used to define the call source of the incoming trunk, the other is the [LAI and GCI] table, used to define the call source of location area/cell.
Generally the call source can be defined as zero by default. If more details are required, define them as required.
Note:
For the tables using the call source code as the index field, such as [Number Prefix Processing], [DN Pre-analysis], [Outgoing Trunk Number Format], [CLI Presentation], the field of the call source code must be filled in with a wild-card value 65534 if the call sources means the same for the processing of the number.
II. Example
In processing emergency numbers such as 117, the basic principle is:
If a subscriber in LA (Location Area) A dials 117, the call should be connected to the emergency center of LA A (e.g.LAI=45618003A3534). If a subscriber in LA B dials 117, the call should be connected to the emergency center of LA B (e.g. LAI = 45618003B3556).
Now assume that both LA A and LA B belong to one MSC.
If a subscriber in LA A dials 117, MSC should convert the number, then route the call to the emergency center of LA A, while when a subscriber in LA B area dials 117, MSC should convert it into another number, then route the call to the emergency center of LA B.
In this case, MSC is required to identify from which LA 117 is sent. MSC fulfils this function by defining different call source codes for the two Las in the [LAI and GCI] table. After call source codes are differentiated, numbers can be converted through “number pre-analysis” part according to different call source codes and 117 prefixes.
Data configurations are as follows:
Figure 4-22 [LAI and GCI] table
Figure 4-23 [Call Source] table
Figure 4-24 [DN Pre-analysis] table
Figure 4-25 [Number change] table
4.2.9 Use of DN Set
II. Example
The principle for configuring MSRN in the [Called Number Analysis] table:
MSRN allocated by the local MSC is generally conFigured as NDC + SN. MSRN allocated by MSC of international other network is conFigured as International Prefix + International number. The format of MSRN allocated by other MSCs of the local network and MSCs of other national network must be conFigured as required by the peer office.
Precondition:
The number format of MSRN in SRI Ack message is CC + NDC + SN (the number attribute is INT). After Black Box conversion described in TP-004, the number format of MSRN before querying [Called Number Analysis] is:
National MSRN: NDC + SN
International MSRN: International Prefix + International number.
The following will introduce the configurations in [Called Number Analysis]:
1) MSRN allocated by the local MSC: Send the number directly to its destination after number analysis in the local MSC. Therefore, conFigure the table as follows: "Service property" = "PLMN local office", and "Called number type" = "MSRN/HON". The
"route selection code" is not required to be conFigured, because it is unnecessary to send the number out.
2) MSRN allocated by other MSCs of the local network and MSCs of other national networks: valid "route selection code" must be conFigured for outgoing route selection. In addition, "Service property" must be conFigured as required by the peer end, i.e. if the peer end requires that the number property should be NAT, it can be conFigured as "PLMN national toll office", and "Called number type" = "MSRN/HON".
3) MSRN allocated by MSC of international other networks: conFigure "Number prefix set" = 9 (The value is defined in "MAP prefix set" in the [Software Parameter] table and the default value is 9). Valid "route selection code" must be conFigured for outgoing route selection. "Service property" is recommended to be conFigured as "PLMN international toll office", and "Called number type" = "MSRN/HON". Moreover, valid "Service index" must be conFigured. When this value is indexed to the [Call Barring Service] table, no items in the "call barring service of caller" field is selected, i.e. no call barring check is performed. The purpose of such configuration is not to perform call barring check to MSRN. For example, although the caller has subscribed to ODB_BOIC service, i.e. international calls barred, this subscriber is still allowed to call a subscriber roaming outside of its home country.
Note:
If the local office is interconnected with the peer office through ISUP, the value of "Nature of address indicator" in IAM message must be correct. This value can be SUB, NAT, INT and UNKNOWN, depending on the configuration of "Service property" in [Called Number Analysis], as shown in the following table:
If the "Nature of address indicator" of the outgoing call cannot meet the requirement of the peer end, it can be changed with the help of the [Outgoing Number Format] table and [Number Change] table.
4.2.11 MSISDN Number Analysis
I. Description
Three types of MSISDN must be conFigured at the local office:
1) MSISDN of local subscribers
2) MSISDN of MS of other national network
3) MSISDN of MS of international network
Among the above-mentioned three types of numbers, only 1) does not need to be sent out of the local MSC and can be directly sent to its home HLR to obtain MSRN. Other two types will be sent out of the local MSC after number analysis.
Since the [Called Number Analysis] table is the core for number analysis, MSISDN analysis is also done in this table.
II. Example
Principle for configuring data in the [Called Number Analysis] table:
MSISDN of MS of the local network is generally conFigured as NDC + SN. MSISDN of MS of international network is conFigured as International Prefix + International number, while the number format of MSISDN of MS of other national networks must be conFigured as required by the peer MSC.
Precondition:
The local office may receive MSISDN from two directions, one from the mobile subscriber side and one from other office direction. After number normalization in number pre-analysis described in TP-003 and TP-004, the number format of MSISDN before querying [Called Number Analysis] should be:
MSISDN of MS of the local network: NDC + SN
MSISDN of MS of other national networks: conFigure it as required by the peer end
MSISDN of MS of international network: International Prefix + International number
The following will introduce configurations in [Called Number Analysis]:
1) MSISDN of MS of the local network: Obtain MSRN after number analysis. ConFigure it as below: "Service property" = "PLMN local office", and "Called number type" = "MSISDN". "Route selection code" is not required, because the call is not necessary to be sent out of the local MSC.
2) MSISDN of MS of other national networks: valid "route selection code" must be conFigured for outgoing route selection. In addition, "Service property" must be conFigured as required by the peer end, i.e. if the opposite end requires that the number property should be NAT, it can be conFigured as "PLMN national toll office". If other properties are required, conFigure with reference to the description in "Note" in TP-010, and "Called number type" = "PSTN".
3) MSISDN of MS of international network: conFigure "Number prefix set" as the value defined in the [Call Source] table. Valid "route selection code" should be conFigured for outgoing route selection. "Service property" is recommended to be conFigured as "PLMN international toll office"; and "Called number type" = "PSTN"."
4.2.12 Analysis of PSTN and Special Number
I. Description
Since PSTN and Special numbers do not belong to local MSC, the local MSC will route them to other MSCs if it receives these numbers.
Since the [Called Number Analysis] table is the core of number analysis, analysis of PSTN and Special number should also be conducted in this table.
After number pre-analysis described in TP-003 and TP-004, generally the number formats of PSTN and Special number before querying [Called Number Analysis] should be:
1) Local PSTN: SN format or Domestic Prefix + Area Code + SN
2) Special number: SN format
3) National toll PSTN: Domestic Prefix + Area Code + SN
4) International toll PSTN: International Prefix + International number
These formats are applicable to common cases. For specific requirements, conFigure them as required.
The property of the outgoing number must be correct. For configuration methods, please refer to the description in the "Notes" in "MSRN Analysis".
II. Example
None.
Figure 4-26 Tables that can define DN set
II. Example
Case 1: There are over 11000 Special numbers, starting with 1 and featuring irregularly, for example, 1XXX.
Handling method: change its DN set through number pre-analysis and process by subdividing it into different number spaces in the called analysis table.
Reason: Special number in this MSC starts with 1. The corresponding processing is to add NDC (NDC = 1) to all MSISDN in SN format during number pre-analysis. In this way, both MSISDN with NDC and Special numbers have the prefix of 1, with overlapped number segments. If Special numbers are not separated by DN set, all short numbers must be completely conFigured in order to distinguish Special number from MSISDN in NDC + SN format. There are about 11000 Special numbers with number completely conFigured. Therefore, this solution is impractical. That is why Special number and MSISDN in NDC + SN format must be divided into two different number spaces through the DN set.
Case 2:
- MSISDN number has two formats: 90 + SN and 590 + SN. When PSTN subscribers dial an MSISDN of an MSC, incoming MSISDN formats with 90 and 590 as prefixes are both allowed. However, 90 and 590 are also the prefixes of local PSTN numbers. In addition to the overlapped prefix, up to 6 digits is overlapped. This situation can be further explained in the example below:
MSISDN = 901234567 (NAT), 5901234567 (NAT).
PSTN number = 901234 (SUB), 590123 (SUB)
Distinguishing numbers with the number prefix only is impractical, for the distinguishing method is to conFigure MSISDN as long as seven digits. Here, using DN set or call source can solve the problem.
The mobile phone cannot be used to dial MSISDNs with prefix of 90 or 590, i.e. numbers with prefix90 or 590 received at the mobile subscriber side are surely PSTN numbers.
Besides, numbers with prefix 90 or 590 received at PSTN side are surely MSISDNs of this MSC, rather than PSTN numbers, as PSTN->PSTN is not allowed to tandem via the local MSC.
Therefore, whether numbers with prefix 90 or 590 are PSTN number or MSISDN can be distinguished with call sources.
First: different call source codes must be defined for each LA and incoming trunk.
Second: in "Call source table", define all call source codes in PSTN exchange direction as one separate DN set (e.g. with the value 1), and define DN sets of all other call source codes with the same value, such as 0.
Then: for MSISDN number, conFigure prefixes 90 and 590 (representing MSISDN) with DN set of “1” and prefixes 90 and 590(representing PSTN) with DN set of “0” in the "Called number analysis table". In this way, when PSTN subscribers call Daewoo Unitel subscribers, what is analyzed is the number space with DN set of 1. This number space with DN set of 1 is used when and only when PSTN subscriber calls mobile subscribers. In all other cases, the number space with DN set of 0 is used.
Finally: conFigure prefixes 90 and 590 (representing MSISDN) with DN set of 1 in the [Called Number Analysis Table]. This is supposed to be the first step, because once all call source codes in PSTN exchange direction are defined as one separate DN set
1 in the "Call source table", the DN set related to this call is 1 by default, i.e. the subsequent table queries are performed with DN set 1.
Several other occasions may occur:
1) No forwarding: After obtaining MSRN subsequently, it is required to query MSRN in the [Called Number Analysis Table]. Therefore, all MSRNs (local office and other offices) of this office with DN set 1 must be conFigured in the [Called Number Analysis Table].
2) Forwarding: after obtaining the forwarded-to number, MSC will query [Country and Zone Code] and [Domestic Toll Zone Code], both of which use the DN set as the index. Therefore, these two tables must have another set of country codes with DN set 1 and domestic toll zone codes with DN set 1. Then MSC will query [DN Pre-analysis] and [Called Number Analysis]. It can be judged in [DN Pre-analysis] that the call source is Call forward side and change the DN set of all numbers received at the Call forward side to 0. In this way, when querying [Called Number Analysis]. It is unnecessary to conFigure all forwarding numbers with DN set 1.