backbone cable
horizontal cable
patch cable
work area cable
BNC
RJ-11
RJ-45
Type F
RJ-11
RJ-45
Type F
3 . When is a straight-through cable used in a network?
when connecting a router through the console port
when connecting one switch to another switch
when connecting a host to a switch
when connecting a router to another router
when connecting a router through the console port
when connecting one switch to another switch
when connecting a host to a switch
when connecting a router to another router
4 . With the use of unshielded twisted-pair copper wire in a network, what causes crosstalk within the cable pairs?
the magnetic field around the adjacent pairs of wire
the use of braided wire to shield the adjacent wire pairs
the reflection of the electrical wave back from the far end of the cable
the collision caused by two nodes trying to use the media simultaneously
5. Which OSI layer is responsible for binary transmission, cable specification, and physical aspects of network communication?
Presentation
Transport
Data Link
Physical
Presentation
Transport
Data Link
Physical
6. An installed fiber run can be checked for faults, integrity, and the performance of the media by using what device?
light injector
OTDR
TDR
multimeter
light injector
OTDR
TDR
multimeter
7. XYZ Company is installing new cable runs on their data network. What two types of cable would most commonly be used for new runs? (Choose two.)
coax
Cat4 UTP
Cat5 UTP
Cat6 UTP
STP
coax
Cat4 UTP
Cat5 UTP
Cat6 UTP
STP
8. What is a possible effect of improperly applying a connector to a network cable?
Data will be forwarded to the wrong node.
Data transmitted through that cable may experience signal loss.
An improper signaling method will be implemented for data transmitted on that cable.
The encoding method for data sent on that cable will change to compensate for the improper connection.
Data will be forwarded to the wrong node.
Data transmitted through that cable may experience signal loss.
An improper signaling method will be implemented for data transmitted on that cable.
The encoding method for data sent on that cable will change to compensate for the improper connection.
9. What are three measures of data transfer? (Choose three.)
goodput
frequency
amplitude
throughput
crosstalk
bandwidth
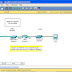
10.
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of Category 5 cable is used to make an Ethernet connection between Host A and Host B?
coax cable
rollover cable
crossover cable
straight-through cable
11. In LAN installations where potential electrical hazards or electromagnetic interference may be present, what type of media is recommended for backbone cabling?
coax
fiber
Cat5e UTP
Cat6 UTP
STP
12. Which fiber connector supports full duplex Ethernet?
* (Third one is the correct one)
13. Which method of signal transmission uses radio waves to carry signals?
electrical
optical
wireless
acoustic
14. Which characteristics describe fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling.
15. Which of the following is a characteristic of single-mode fiber-optic cable?
generally uses LEDs as the light source
relatively larger core with multiple light paths
less expensive than multimode
generally uses lasers as the light source
16. What is considered a benefit of wireless as a media choice?
more host mobility
lower security risks
reduced susceptibility to interference
less impact of the surroundings on the effective coverage area
17. What characteristic of UTP cable helps reduce the effects of interference?
the metal braiding in the shielding
the reflective cladding around core
the twisting of the wires in the cable
the insulating material in the outer jacket
18. What is a primary role of the Physical layer in transmitting data on the network?
create the signals that represent the bits in each frame on to the media
provide physical addressing to the devices
determine the path packets take through the network
control data access to the media
goodput
frequency
amplitude
throughput
crosstalk
bandwidth
10.
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of Category 5 cable is used to make an Ethernet connection between Host A and Host B?
coax cable
rollover cable
crossover cable
straight-through cable
11. In LAN installations where potential electrical hazards or electromagnetic interference may be present, what type of media is recommended for backbone cabling?
coax
fiber
Cat5e UTP
Cat6 UTP
STP
12. Which fiber connector supports full duplex Ethernet?
13. Which method of signal transmission uses radio waves to carry signals?
electrical
optical
wireless
acoustic
14. Which characteristics describe fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding and twisting to protect data.
It has a maximum speed of 100 Mbps.
It is the most expensive type of LAN cabling.
15. Which of the following is a characteristic of single-mode fiber-optic cable?
generally uses LEDs as the light source
relatively larger core with multiple light paths
less expensive than multimode
generally uses lasers as the light source
16. What is considered a benefit of wireless as a media choice?
more host mobility
lower security risks
reduced susceptibility to interference
less impact of the surroundings on the effective coverage area
17. What characteristic of UTP cable helps reduce the effects of interference?
the metal braiding in the shielding
the reflective cladding around core
the twisting of the wires in the cable
the insulating material in the outer jacket
18. What is a primary role of the Physical layer in transmitting data on the network?
create the signals that represent the bits in each frame on to the media
provide physical addressing to the devices
determine the path packets take through the network
control data access to the media