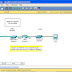
Refer to the
exhibit. The network in the exhibit is fully operational. What two statements
correctly describe the routing for the topology that is shown? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.0.2 is the next-hop address that is used by R3 to
route a packet from the 10.0.0.0 network to the 172.16.0.0 network.
- 10.0.0.1
is the next-hop address that is used by R1 to route a packet from the
192.168.12.0 network to the 10.0.0.0 network.
- 192.168.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R1 to route a packet from the 192.168.12.0 network to the 172.16.0.0 network.
- 172.16.0.1
is the next-hop address that is used by R3 to route a packet from the 10.0.0.0
to the 172.16.0.0 network.
- 192.168.0.1 is the next-hop address that is used by R2 to
route a packet from the 172.16.0.0 network to the 192.168.12.0 network.
- 192.168.0.2
is the next-hop address that is used by R2 to route a packet from the
172.16.0.0 network to the 192.168.12.0 network.
2-


Refer to the
exhibit. Using the network in the exhibit, what would be the default gateway
address for host A in the 192.133.219.0 network?
- 192.135.250.1
- 192.31.7.1
- 192.133.219.0
- 192.133.219.1
3- Which
three statements are true about routes and their use? (Choose three.)
- If no
route to the destination network is found, the packet is returned to the
previous router.
- If the destination network is directly connected, the
router forwards the packet to the destination host.
- If
multiple network entries exist for the destination network, the most general
route is used to forward the packet.
- If no route exists for the destination network and a
default route is present, the packet is forwarded to the next-hop router.
- If the originating host has a default gateway configured, the
packet for a remote network can be forwarded using that route.
- If a host
does not have a route manually configured for the destination network, the host
will drop the packet.
4- Which
intermediary devices could be used to implement security between networks?
(Choose two.)
- router
- hub
- switch
- firewall
- access
point
- bridge
5- What type
of routing uses information that is manually entered into the routing table?
- dynamic
- interior
- static
- standard
6-


Refer to the
exhibit. A network administrator notices that there are too many broadcasts on
the network. What two steps can the network administrator take to resolve this
problem? (Choose two.)
- Replace S2 with a router.
- Place all
servers on S1.
- Disable
TCP/IP broadcasts.
- Subnet the 192.168.0.0 /24 network.
- Disable
all unused interfaces on the switches.
7-

- 10.10.10.26
- 127.0.0.1
- 10.10.10.6
- 10.10.10.1
- 224.0.0.0
8- If the
default gateway is configured incorrectly on the host, what is the impact on
communications?
- The host
is unable to communicate on the local network.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on the local
network, but is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
- The host
can communicate with other hosts on remote networks, but is unable to
communicate with hosts on the local network.
- There is
no impact on communications.
9- What is
the purpose of a default gateway?
- physically
connects a computer to a network
- provides a
permanent address to a computer
- identifies
the network to which a computer is connected
- identifies
the logical address of a networked computer and uniquely identifies it to the
rest of the network
- identifies the device that allows local network computers
to communicate with devices on other networks
10- What
statement describes the purpose of a default route?
- A host
uses a default route to transfer data to another host on the same network
segment.
- A host
uses a default route to forward data to the local switch as the next hop to all
destinations.
- A host
uses a default route to identify the Layer 2 address of an end device on the
local network.
- A host uses a default route to transfer data to a host
outside the local network when no other route to the destination exists.
11- What are
three common problems with a large network? (Choose three.)
- too few
broadcasts
- performance degradation
- security issues
- limited
management responsibility
- host identification
- protocol
compatibility
12- In a
connectionless system, which of the following is correct?
- The
destination is contacted before a packet is sent.
- The destination is not contacted before a packet is sent.
- The
destination sends an acknowledgement to the source that indicates the packet
was received.
- The
destination sends an acknowledgement to the source that requests the next
packet to be sent.
13- Which
portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host
portion
- broadcast
address
- network portion
- gateway
address
14- What is
a component of a routing table entry?
- the MAC
address of the interface of the router
- the
destination Layer 4 port number
- the
destination host address
- the next-hop address
15-

- 3
- 4
- 5
- 7
- 8
- 11
16- What
information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and
destination MAC
- source and
destination application protocol
- source and
destination port number
- source and destination IP address
17- In an
IPv4 environment, what information is used by the router to forward data
packets from one interface of a router to another?
- destination network address
- source
network address
- source MAC
address
- well known
port destination address
18- What two
characteristics are commonly associated with dynamic routing protocols? (Choose
two.)
- require no
device configuration
- provide routers with up-to-date routing tables
- require
less processing power than static routes require
- consume bandwidth to exchange route information
- prevent
manual configuration and maintenance of the routing table
19- Which IP
packet field will prevent endless loops?
- type-of-service
- identification
- flags
- time-to-live
- header
checksum
20- When the
destination network is not listed in the routing table of a Cisco router, what
are two possible actions that the router might take? (Choose two.)
- The router
sends an ARP request to determine the required next hop address.
- The router discards the packet.
- The router
forwards the packet toward the next hop indicated in the ARP table.
- The router
forwards the packet to the interface indicated by the source address.
- The router forwards the packet out the interface indicated
by the default route entry.
21- What are
the key factors to consider when grouping hosts into a common network? (Choose
three.)
- gateways
- purpose
- physical
addressing
- software
version
- geographic location
- ownership