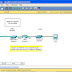
Based on the call flow, the number analysis flow can be divided into the following procedures:
All the number analysis procedures are shown in Figure 1.
- Number preprocessing in the mobile originated call (MOC) flow
- Number preprocessing in the incoming trunk call flow
- Public number preprocessing
- Number processing for interaction with the HLR
- Number processing for interaction with the SCP
- Core procedure of number analysis
- Number processing in the mobile terminated call (MTC) flow
- Number processing in the outgoing trunk call flow
- Analysis of numbers in CDR
All the number analysis procedures are shown in Figure 1.
The types of calls processed by the MSC server can be categorized as follows:
- By call direction, calls are classified into outgoing originated calls, intra-MSC calls, transit calls, and incoming terminated calls.
- By call source, calls are classified into MOCs and incoming trunk calls.
- MOCs are classified into outgoing originated calls and intra-MSC calls.
- Incoming trunk calls are classified into transit calls and incoming terminated calls.
- By call termination direction, calls are classified into MTCs and outgoing trunk calls.
- MTCs are classified into intra-MSC calls and incoming terminated calls.
- Outgoing trunk calls are classified into transit calls and outgoing originated calls.
- Number Preprocessing in the MOC Flow: The MSC server preprocesses the called number in an MOC based on the calling and called subscriber attributes, determines the call source, and then classifies the call. This facilitates the subsequent public number preprocessing and core procedure of number analysis.
- Number Preprocessing in the Incoming Trunk Call Clow: The MSC server preprocesses the called number in an incoming terminated call based on the calling and called subscriber attributes, determines the call source, and then classifies the call. This facilitates the subsequent public number preprocessing and core procedure of number analysis.
- Public Number Proprocessing: This procedure is indispensable to all call types. It is used to change numbers before the MSC server starts the core procedure of number analysis.
- Core Procedure of Number Analysis: This procedure is indispensable to all call types. It determines the next procedure based on the analysis of the called number.
- If the called number type is MSISDN, the MSC server requests the MSRN from the HLR, which involves number processing in the SRI-REQ flow and number processing in the SRI-ACK flow.
- If the called number type is PSTN or unknown, the MSC server starts outgoing call routing and number processing in the outgoing trunk call flow.
- If the called number type is MSRN, the MSC server checks whether this MSRN is allocated by the local VLR through Core Procedure of Number Analysis and then determines whether the call is an MTC or outgoing trunk call based on the check result.
- Number processing for interaction with the HLR consists of Number Processing in the SRI-REQ Flow and Number Processing in the SRI-ACK Flow: The MSC server normalizes the called number sent to the HLR for obtaining the MSRN and then normalizes the MSRN returned by the HLR.
- Number processing for interaction with the SCP consists of Number Processing in the CAMEL Event Reporting Flow and Number Processing in the CAMEL Event Receiving Flow: The MSC server normalizes the number sent to the SCP, checks data configuration to determine whether to trigger CSI, and normalizes the number sent by the SCP.
- Number Processing in the MTC Flow: The MSC server normalizes the number sent to the terminal in an MTC.
- Number Processing in the Outgoing Trunk Call Flow: The MSC server normalizes the number sent to the peer MSC server in an outgoing trunk call.
- Change of Numbers in CDRs: The MSC server normalizes the numbers in a CDR for charging.