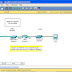
If two offices have direct voice path, one office is called the office direction of the other. For example, there are direct voice channels between office A and office B, office A and office C, and office A and office D, as shown in Figure 1. It means that office B is an office direction of office A, office C is an office direction of office A, and office D is an office direction of office A. In addition,
because there is no direct voice channel between office B and office C, office C is not an office direction of office B. Also, office B is not an office direction of office C.
In the MSOFTX3000, an office direction is defined by a unique name, so that it can be easily identified. For example, for office A in Figure 1, office direction from A to D can be defined as 1, office direction from A to B can be defined as 2, and office direction from A to C can be defined as 3.
because there is no direct voice channel between office B and office C, office C is not an office direction of office B. Also, office B is not an office direction of office C.
In the MSOFTX3000, an office direction is defined by a unique name, so that it can be easily identified. For example, for office A in Figure 1, office direction from A to D can be defined as 1, office direction from A to B can be defined as 2, and office direction from A to C can be defined as 3.
Sub-Route
If a direct voice channel or an alternative channel exists between two offices, it means a sub-route exists between the two offices. The direct voice channel is the direct sub-route and the alternative channel is the alternative sub-route. For example, there are three sub-routes between office A and office D as shown in Figure 1:- Sub-route 1 is a direct sub-route from office A to office D.
- Sub-route 2 is an alternative sub-route from office A to office D through office B.
- Sub-route 3 is an alternative sub-route from office A to office D through office C.
Route
A route is a set of all sub-routes from local office to a destination office. A route contains multiple sub-routes and different routes may contain the same sub-routes. For example, in Figure 1:- The route from office A to office D contains sub-route 1, sub-route 2 and sub-route 3. The direct sub-route is sub-route 1.
- The route from office A to office B contains sub-route 1, sub-route 2 and sub-route 3. The direct sub-route is sub-route 2.
- The route from office A to office C contains sub-route 1, sub-route 2 and sub-route 3. The direct sub-route is sub-route 3.