I. Chapter1: Relative Concept
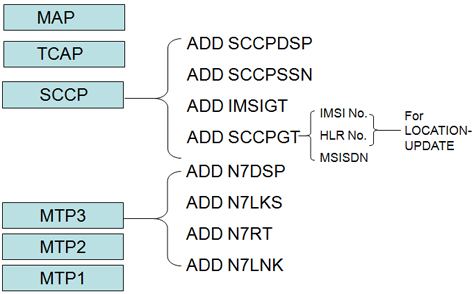
MAP
MAP is mobile application part,MAP protocol is used to help MS to implement roaming and other functions then the mobile network entities can inter-communicate signaling with each other (mobility management). Network entities contain MSC Server, VLR, SGSN, HLR, SMC etc. In UMTS network,C, D, E, G interface can transmit MAP signaling,usually we call these interfaces as MAP interfaces.
Explanation
Now, we usually use the C/D interface based on the TDM.
2. MTP3 layer data Configuration:
1) add MTP DPC ADD N7DSP( HLR is DPC)
2) add MTP link set ADD N7LKS( to HLR)
3) add MTP route ADD N7RT ( to HLR)
4) add MTP link ADD N7LNK ( to HLR)
General Number Analysis Flow
Detail:
III. Chapter3: Example of Configuration
III. Chapter3: Example of Configuration
This example is to add a local HLR, which is directly connected to the MSC through E1 line. (Based on TDM) Physical Connected:
ADD N7LKS: LSX=2, ASPX=2, LSNAME="TO HLR";
ADD N7RT: LSX=2, DPX=2, RTNAME="TO HLR";
ADD N7LNK: MN=22, LNKN=2, LNKNAME=“HLR”, LNKTYPE=0, TS=48(ACCORDING PLAN), LSX=2, SLC=0, SLCS=0;
ADD SCCPDSP: DPX=2, NI=NAT, DPC="BFF09", DPNAME="HLR", SHAREFLAG=NONE;
ADD SCCPSSN: SSNX=3, NI=NAT, SSN=SCMG, SPC=“BFF09”, OPC=“3000”, SSNNAME=“SCMG-HLR”;(LOCAL TO REMOTE)
ADD SCCPSSN: SSNX=4, NI=NAT, SSN=HLR, SPC="BFF09", OPC="3000", SSNNAME="HLR-HLR"; (LOCAL TO REMOTE)
ADD IMSIGT: MCCMNC=“46009”, CCNDC=“86139”(E.212 to E.214);
ADD SCCPGT: GTX=1, GTNAME=“HLR-IMSIGT”, NUMPLAN=ISDNMO(NECESSARY), ADDR=K'86139, RESULTT=LSPC2, SPC="BFF09";
ADD SCCPGT: GTX=2, GTNAME="HLR-GT", NUMPLAN=ISDN, ADDR=K'8613817550000, RESULTT=LSPC2, SPC="BFF09";
ADD SCCPGT: GTX=3, GTNAME="HLR-MSISDN", NUMPLAN=ISDN, ADDR=K'861390755, RESULTT=LSPC2, SPC="BFF09";
Chapter Summary
This chapter give a whole data configuration to HLR.
Please pay high attention on the preparing data, because some data must be same with remote office.
Check MTP Relative Configuration
Check all MTP configuration
Result of Display MTP Relative Information
DSP N7DSP normal status:
“Accessibility = Accessible”
DSP N7RT normal status:
“Route Information = Healthy
Transfer Allowed In Service
……”
DSP N7LNK normal status:
“Status = In Use, Healthy,
Not Blocked,
Activated,
……”
To manage prohibited MTP link, the link will be unavailable ——INH N7LNK
Release manage prohibited MTP link , the link will be unavailable ——UIN N7LNK
To activate the MTP link ——ACT N7LNK
To deactivate the MTP link ——DEA N7LNK